It is a condition where the endometrial tissue that normally lines
the inside of the uterus grows outside the uterus, either on the Ovaries
or Fallopian tubes. In normal situations, that is, when the endometrial tissue grows
inside the uterus like it's supposed to, the endometrial tissues are
usually filled with blood vessels in preparation for pregnancy and in
the absence of pregnancy, part of the endometrial tissue breaks down,
causing menstrual bleeding. In the case of endometriosis, the same thing
happen with the tissue that has grown outside of the uterus, it becomes
filled with blood vessels and is broken down and shed as menstrual
bleeding. For some women affected with the condition, it could be painful while
some don't even feel pain at all and the degree of pain varies; from
mild to severe. Endometriosis causes pain, although 20–25% of patients are asymptomatic.Source While the exact cause is not clear, there are theories and also risk
factors that have been thought to lead to the development of
endometriosis Retrograde Menstruation: This theory was first proposed by John
A. Sampson. It is the most widely accepted theory for the formation of
endometriosis. The theory suggests that during menstrual flow, menstrual
blood containing endometrial cells flow back through the Fallopian tube
into the peritoneal cavity. The cells then begin to attach themselves
to the lining of the abdominal cavity, then start to grow, thicken, and
bleed during each menstrual cycle. Peritoneal cells transformation: The theory proposes that
hormones or immune factors induce the transformation of peritoneal cells
into endometrial cells. It is also known as the "induction theory". Embryonic cell transformation: this theory proposes that hormones
such as estrogen could transform embryonic cells into endometrial cell
implants during puberty Risk factors These factors increase the chances of being affected with endometriosis. There is a six fold increased incidence of the condition in women with an affected first degree relative Other factors include; Never giving birth Early start of menstruation Delayed menopause Medical conditions that prevents normal menstrual flow out of the body. Infertility and pain are the main symptoms of endometriosis. Infertility: About 40% of women affected with endometriosis are
infertile. The determination of the disease is most times dependent on
the stage of the disease, with the later stage disease leading to
distorted pelvic anatomy and adhesions which in turn increases the
chances of infertility. Pelvic pain: Most times, this pain is often associated with the
menstrual period. It most times affect the lower back and legs too. The
pain starts before the menstrual period and continues in the course of
the menstrual flow. Many women tend to disregard excess menstrual pain but it might
involve other complications so it's best to complain to the doctor early
enough Pain during or after sex Pain during bowel movement Excessive bleeding either during menstrual flow or between periods. The severity of the pain experienced is not an indication of the
stage of the condition. Some women might experience extensive pain but
still have mild endometriosis while some with advanced endometriosis
experience little pain. After experiencing these symptoms, the best thing to do is to book an
appointment with your doctor, so as to undergo some tests. The tests
that could be carried out by your doctor include: Pelvic examination : During this exam, your doctor manually feels
for abnormalities such as cysts around your pelvic area. It is usually
impossible to feel small areas of endometriosis unless they've formed a
cyst. Ultrasound : This test doesn't definitely tell whether you're
affected with endometriosis but it can identify cysts associated with
endometriosis. A device called a transducer is used to capture images
from inside the body. It is either just pressed against the abdomen or
inserted into the vagina. Laparoscopy: To be certain you have endometriosis, your doctor
then refers you to a surgeon for a surgical procedure known as
laparoscopy. During the surgery, a tiny incision is made near the navel,
then a viewing instrument (a laparoscope) is inserted to check for the
location and size of the endometriosis and this helps in choosing the
best treatment option. After diagnosis,depending on the severity of the condition, the
doctor recommends two options for treatment; Medication or Surgery. Medications Pain Medication Hormone therapy During the menstrual cycle, hormones are usually not stable and this
causes the thickening and break down of endometrial cells. Supplementary
hormones could help to slow the growth of endometrial cells and even
stop new growth. This treatment option is only effective for as long as
you keep taking the hormone supplements. Types of supplements that could
be used include: Hormonal contraceptives such as birth control pills, patches and vaginal rings. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (Gn-RH) agonists and antagonists that act to reduce estrogen levels and prevent menstruation. Danazol which acts by suppressing the growth of the endometrium
by stopping the production of ovarian-stimulating hormones which
prevents menstruation and the symptoms of endometriosis. Surgery Assisted Reproductive Technology could be used if the conservative surgery is not successful. Hysterectomy As a last resort, especially in patients that experience severe pain,
hysterectomy is recommended. It involves the total removal of the
uterus, cervix and ovaries too. Conclusion While endometriosis is a condition that could be managed and treated,
it still kills. This is due to the ignorance of many about the
condition, therefore, awareness of endometriosis should be increased and
this will curb the mortality rate. Thank you for taking time to read this!!! Sources Endometriosis: symptoms and causes A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015First of, what is endometriosis??
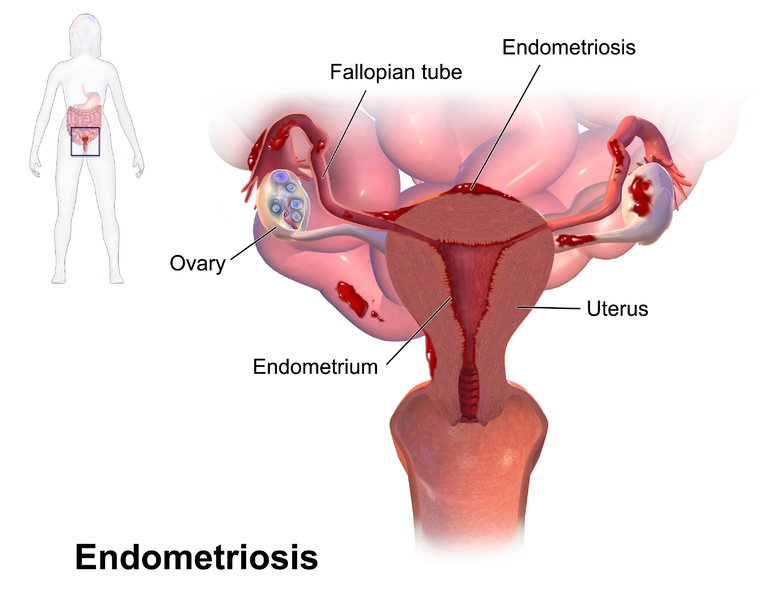
An
illustration depicting the growth of endometriosis on the ovary, uterus
and fallopian tube: image from wikimedia licensed under CC3
What causes endometriosis??
It has been proposed that it's development is similar to that of cancer,
in that it results from a series of multiple hits within target genes.
The initial mutation in this case could be somatic or heritable.SourceSymptoms of endometriosis
How is it diagnosed??
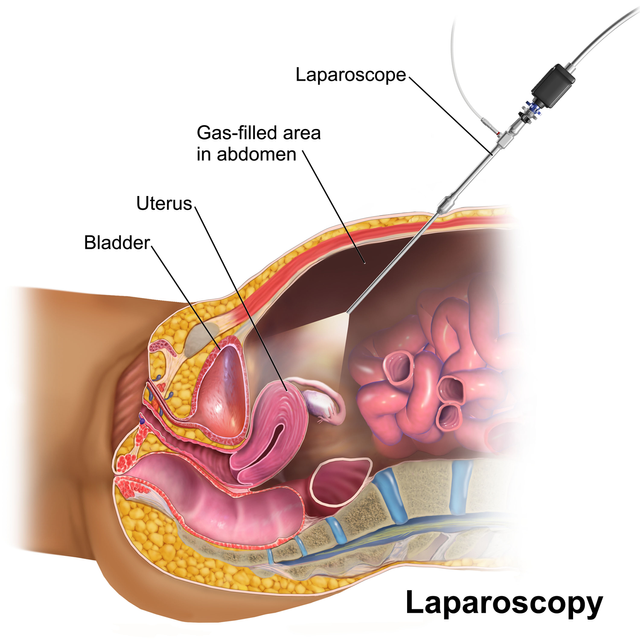
An illustration showing the laparoscope being used: image from wikimedia licensed under CC3.What are the treatment options??
Over the counter pain relievers such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs (NSAIDs), Ibuprofen or naproxene could be recommended by the
doctor.
Conservative Surgery
If these medications don't reduce the pain of endometriosis, Surgery is now considered.
Conservative surgery is usually done to remove as much endometrial
tissue as possible while protecting the uterus and ovaries so as to
increase the chances of pregnancy. The down side to the conservative
surgery is that there is a chance of the pain and endometriosis
recurring.
It is better to consult with a doctor you're familar with and it is also
advisable to get a second opinion before deciding treatment options.
0